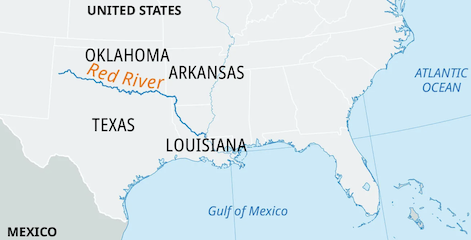
Red River. The name given to several rivers worldwide, with two of the most prominent being the Red River of the South in the United States and the Red River of the North, which forms part of the U.S.-Canada border.
Red River of the South
- Location: United States (Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisiana)
- Length: Approximately 1,360 miles (2,190 km)
- Source: Eastern New Mexico
- Mouth: Mississippi River via the Atchafalaya River
- Significance: The river played a crucial role in early American frontier history, serving as a transportation route and natural boundary. It is known for its reddish color, attributed to high sediment content.
Red River of the North
- Location: United States (Minnesota, North Dakota) and Canada (Manitoba)
- Length: Approximately 550 miles (885 km)
- Source: Confluence of the Bois de Sioux and Otter Tail Rivers
- Mouth: Lake Winnipeg
- Significance: This river is notable for its role in agriculture and its history of severe flooding, particularly affecting the city of Fargo, North Dakota, and Winnipeg, Manitoba.
Other Red Rivers
Several other rivers around the world share the name Red River, including:
- Red River (Vietnam and China) – A major river in Southeast Asia, flowing from China through Vietnam into the Gulf of Tonkin.
- Red River (India) – Also known as the Brahmaputra in parts of its course.
- Red River (Australia) – A small river found in parts of Western Australia.
Cultural and Historical Impact
Red Rivers have played essential roles in regional histories, economies, and geographies. They have influenced settlement patterns, trade routes, and ecological developments in their respective regions.