Navigating Prostate Cancer
New York, N.Y. — Prostate cancer ranks among the most frequent cancers affecting men globally, with over 1.4 million new cases annually.
Despite its prevalence, myths and confusion persist.
This article offers a clear overview of prostate cancer, exploring its origins, signs, and treatment paths, while dispelling common misconceptions to empower those at risk or their loved ones with essential knowledge.
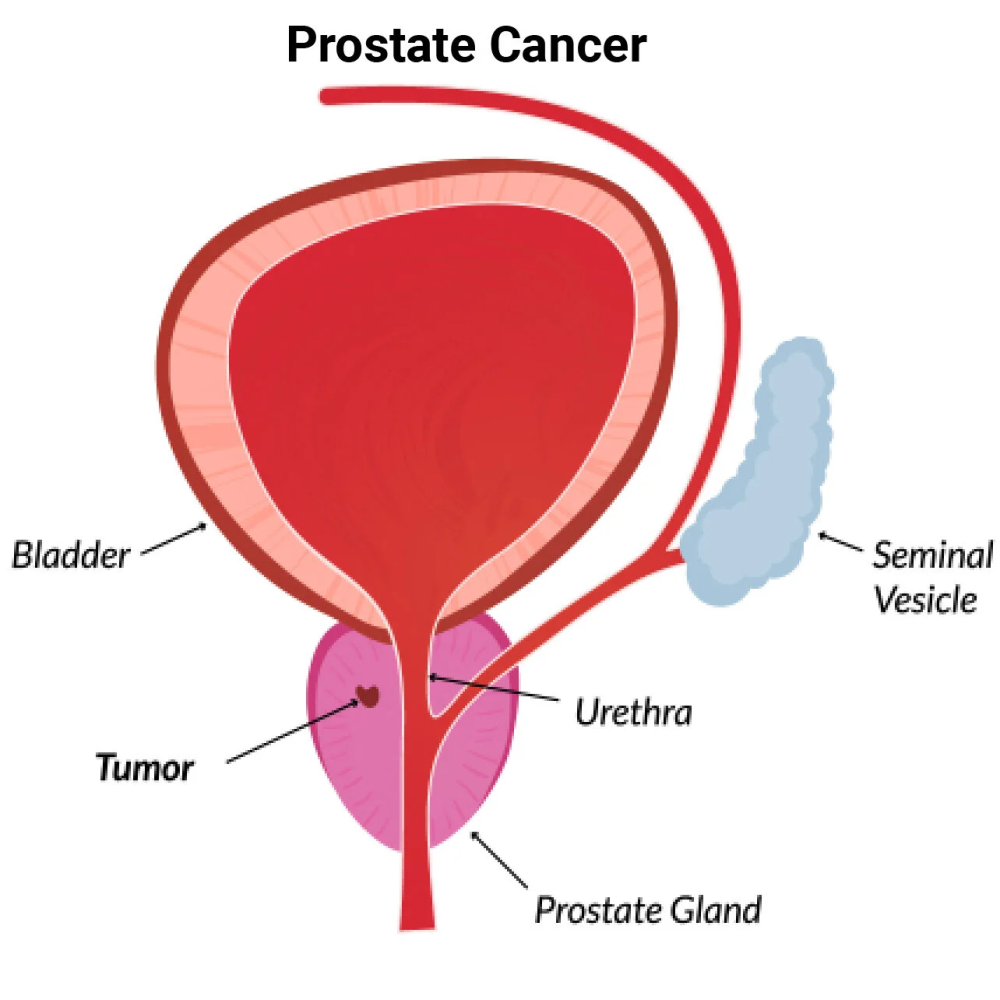
Prostate cancer originates in the prostate gland, a small organ beneath the bladder that aids sperm production. Key risk factors include advancing age—particularly beyond 50—and a family history of the disease.
As it progresses, symptoms may include urinary difficulties, blood in urine or semen, pelvic discomfort, erectile challenges, and, in advanced stages, weight loss or leg swelling.
Insights into Causes, Symptoms, and Care
Detection often begins with a PSA blood test, measuring prostate-specific antigen levels, though elevated results can stem from non-cancerous conditions like inflammation or benign growths. Imaging, such as MRI, may follow, aiding diagnosis without immediate biopsy.
Prostate cancers vary by cell type.
The most common, adenocarcinoma, makes up about 95% of cases and grows slowly, while small cell carcinoma, less than 5%, is more aggressive. Rarer forms include sarcomas (from connective tissue), neuroendocrine tumors (from hormone cells), and transitional cell carcinomas (from bladder lining spread). Treatment hinges on the type—adenocarcinoma often responds to surgery or radiation, while aggressive forms may need chemotherapy.
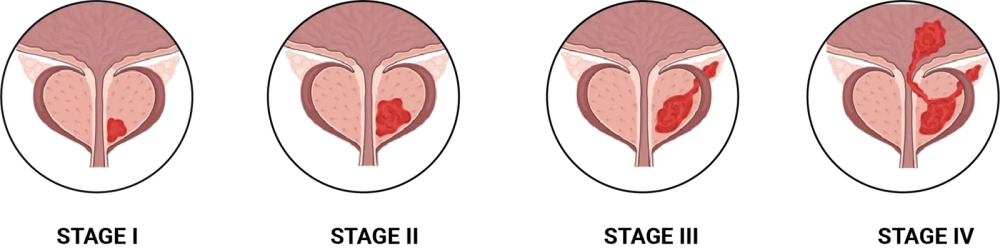
Staging, using the TNM system (Tumor, Nodes, Metastasis), ranges from Stage I (confined, small tumor) to Stage IV (spread to bones or organs). Early stages may warrant monitoring, while advanced cases demand prompt intervention.
Symptoms like frequent urination or pain guide diagnosis, with options including active surveillance for low-risk cases, surgical removal, radiation, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy, tailored to the patient’s health and preferences.
Debunking myths, prostate cancer isn’t always aggressive—many cases progress slowly, allowing for watchful waiting. Regular screening and a healthy lifestyle—exercise, balanced diet, and avoiding smoking or excess alcohol—can lower risks. Consult a healthcare provider for symptoms or concerns to ensure timely, informed care.
Prostate Health Matters: Exploring Causes and Care Strategies (March 5, 2025)